The McKinsey Global Institute (MGI) is a pretty high falutin’ outfit. It’s the business and economics research arm of McKinsey & Company. Not focused so much on middle-market HR folks, it publishes a wealth of well-researched papers that focus on the evolving global economy. Highly scientific in their approach and academic in their tone, they publish some great content. It’s tough slogging from an average professional’s reading perspective, but if you hang in, it’s worth it. It’s McKinsey, for Pete’s sake.
A June 2017 publication caught my eye: Artificial Intelligence, The Next Digital Frontier? is a long (80 pages) read, but a fascinating read. And it takes a deep dive into the investment in artificial intelligence (AI), how it is being deployed, and its potential to disrupt organizations and business. I like MGI research because it isn’t sponsored by any other institution, which fits MGI’s mission which is “to help business and policy leaders understand the forces transforming the global economy identify strategic imperatives, and prepare for the next wave of growth.”
The brief of this “discussion paper” includes:
-
AI investment is growing fast, dominated by digital giants such as Google and Baidu.
-
AI adoption outside the tech sector is at an early, experimental stage.
-
Adoption patterns show a growing gap between early adopters and others.
-
Early evidence suggests that AI can deliver real value to serious adopters and can be a powerful force for disruption.
-
Companies cannot delay advancing their digital journeys, including AI.
-
AI promises benefits, but also poses urgent challenges that cut across firms, developers, government, and workers.
By looking at the contents page, you can see the flow of the information and delve first into the parts that are most interesting to you. The paper has 3 sections and 2 appendices:
-
Artificial intelligence is getting ready for business, but are businesses ready for AI?
-
Artificial intelligence promises to boost profits and transform industries
-
Businesses, developers and governments need to act now to realize AI’s full potential.
Appendix A: Five case studies
- Retail
- Electric utility
- Manufacturing
- Health care
- Education
Appendix B: Technical appendix
I’m personally fascinated that in picking 5 sectors, Education made the grade. But truly, if ever there was a sector ripe for disruption, it’s the Education sector.
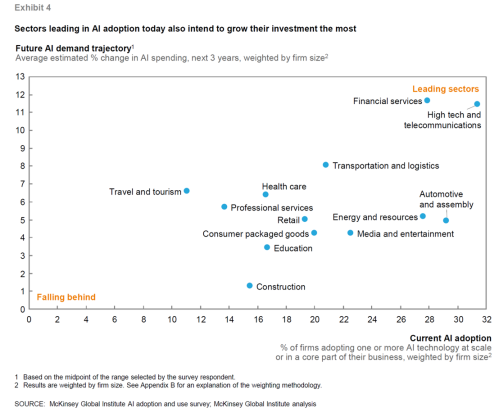
The following is one of the very interesting graphs/charts included in the paper:
It’s fascinating to see the level of current AI adoption compared with the AI demand trajectory. Of particular interest is MGI’s opinion that “variation of adoption within industries will be even larger than between industries.” That means, I think, that the AI divide – the haves and have nots – won’t be so much defined by industry as by early adoption status and investment. I can see a future bifurcated by this variable. This means that every organization, regardless of industry, has the ability now to decide to on the side of early adoption and industry disruption.
This is a fascinating paper. You might not read every word, but the whole AI discussion will be framed for you in a way that will allow you to participate – and even lead – in a meaningful way.
It’s a good discussion paper. It’s McKinsey. Read it.